|
2D autocorrelations
|   |
List of 2D autocorrelations calculated by DRAGON
2D autocorrelations calculated by DRAGON are spatial autocorrelations calculated on a H-depleted molecular graph weighted by atom physico-chemical properties (i.e. the atom weightings w) and include:
2D autocorrelations are molecular descriptors which describe how a considered property is distributed along a topological molecular structure.
The Broto-Moreau autocorrelation ATSkw, w being the atomic property used to weight the molecular graph and k the lag, is evaluated by considering separately all the contributions of each different path length (lag) in the molecular graph, as collected in the topological distance matrix. In other words, the total spatial autocorrelation at lagk ATSkw is obtained by summing all the products wi×wj of all the pairs of atoms i and j, for which the topological distance equals the lag as:
![]()
where nSK is the number of non-Hydrogen molecule atoms and dij is the Kronecker delta (dij = 1 if dij = k, zero otherwise, dij being the topological distance between two considered atoms).
The Moran autocorrelation MATSkw, w being the atomic property used to weight the molecular graph and k the lag, is calculated by applying the Moran coefficient to the molecular graph:
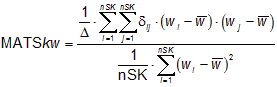
where wi is any atomic property, ![]() is its average value on the molecule, nSK is the number of non-Hydrogen atoms, dij is the Kronecker delta (dij = 1 if dij = k, zero otherwise, dij being the topological distance between two considered atoms). D is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, i.e. the number of atom pairs at distance equal to k. Moran coefficient usually takes value in the interval [-1,+1]. Positive spatial autocorrelation corresponds to positive values of the coefficient whereas negative spatial autocorrelation produces negative values.
is its average value on the molecule, nSK is the number of non-Hydrogen atoms, dij is the Kronecker delta (dij = 1 if dij = k, zero otherwise, dij being the topological distance between two considered atoms). D is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, i.e. the number of atom pairs at distance equal to k. Moran coefficient usually takes value in the interval [-1,+1]. Positive spatial autocorrelation corresponds to positive values of the coefficient whereas negative spatial autocorrelation produces negative values.
The Geary autocorrelation GATSkw, w being the atomic property used to weight the molecular graph and k the lag, is calculated by applying the Geary coefficient to the molecular graph:
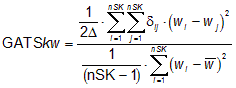
where wi is any atomic property, ![]() is its average value on the molecule, nSK is the number of non-Hydrogen atoms, dij is the Kronecker delta (dij = 1 if dij = k, zero otherwise, dij being the topological distance between two considered atoms). D is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, i.e. the number of atom pairs at distance equal to k. Geary coefficient is a distance-type function varying from zero to infinite. Strong spatial autocorrelation produces low values of this index; moreover, positive autocorrelation translates in values between 0 and 1 whereas negative autocorrelation produces values larger than 1; therefore, the reference "no correlation" is coefficient value equal to 1.
is its average value on the molecule, nSK is the number of non-Hydrogen atoms, dij is the Kronecker delta (dij = 1 if dij = k, zero otherwise, dij being the topological distance between two considered atoms). D is the sum of the Kronecker deltas, i.e. the number of atom pairs at distance equal to k. Geary coefficient is a distance-type function varying from zero to infinite. Strong spatial autocorrelation produces low values of this index; moreover, positive autocorrelation translates in values between 0 and 1 whereas negative autocorrelation produces values larger than 1; therefore, the reference "no correlation" is coefficient value equal to 1.
To obtain uniform-length descriptors for a set of molecules DRAGON calculates 2D autocorrelation descriptors from lag 1 to 8. Autocorrelations at lag 0 are not provided being a simple sum of the squares of atomic properties. Atomic properties w used to weight molecular graphs are: carbon-scaled atomic mass (m), carbon-scaled atomic van der Waals volume (v), carbon-scaled atomic Sanderson electronegativity (e) and carbon-scaled atomic polarizability (p).
Finally, to avoid too large numbers, a logarithmic transformation of the Moreau-Broto autocorrelation values (ATS) is performed as ln(1 + value).