|
Functional group counts
|   |
List of functional group counts calculated by DRAGON
These are simple molecular descriptors defined as the number of specific functional groups in a molecule. They are calculated by knowing the molecular composition and atom connectivities.
DRAGON calculates 154 functional group counts; see the list for more explanation. A lot of attention has been paid in distinguishing whether the same functional group belongs to an aliphatic or an aromatic molecular fragment.
The letter R in the descriptor symbols represents any group linked through carbon, the letter X refers to halogens, b represents benzene, Ar any aromatic group linked through carbon, and r any non-aromatic ring, = and # represent double and triple bonds, respectively.
The number of terminal primary C(sp3), C(sp2) and C(sp) is determined by adding up the carbons for which the difference between connectivity (i.e. the number of bonded atoms) and number of bonded terminal groups is equal to 1. A group is identified as a terminal group if it has connectivity of 1 (e.g. H and halogens) or if it is a non-carbon atom bonded only to atoms with connectivity of 1, excluding the reference carbon (e.g. OH, SH, NH2, etc.).
The number of non-aromatic conjugated C(sp2) (nCconj) is the summation of all the sp2-hybridized C belonging to any conjugated system, excluding aromatic rings. The considered conjugated systems are those including the following atom types:
=C<, =N-, =P-, =B-, =N<, =P<, =S<, >P(=)-, >B(=)-, =O, =S.
The number of donor atoms for H-bonds (nHDon) is a measure of the hydrogen-bonding ability of a molecule expressed in terms of number of possible hydrogen-bond donors. Specifically, it is calculated by adding up the hydrogens bonded to any nitrogen and oxygen in the molecule.
The number of acceptor atoms for H-bonds (nHAcc) is a measure of the hydrogen-bonding ability of a molecule expressed in terms of number of possible hydrogen-bond acceptors. Specifically, it is calculated by adding up any nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine, excluding N with positive formal charge, higher oxidation states and pyrrolyl form of nitrogen.
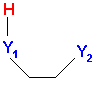
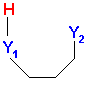
The number of intramolecular H bonds (nHBonds) is a new molecular descriptor, which adds up any atom pairs Y1Y2 in the molecule so that Y1 can be B, N, O, Al, P, S with at least one bonded hydrogen and Y2 can be N, O, F. Moreover, to have an intramolecular H bond the topological distance between Y1 and Y2 must be 3 or 4 and the geometrical distance between Y2 and H bonded to Y1 must be in the range (1; 2,7). Note that to calculate this descriptor, which is based on geometrical distances between atoms, it's necessary to select the geometrical descriptor block along with the functional groups (this only holds for Dragon for Windows).